Testosterone in Men: Functions, Deficiency Side Effects, and How to Increase Levels
As someone 34 years old when this article was written, I can clearly say, based on my blood work and personal experience, how important it is to have healthy testosterone levels.
I see many men in their mid-30s, 40s, or 50s with symptoms of low testosterone. Signs like lack of energy, poor sleep, inability to deal with daily stress, and even depression represent a common struggle amongst today's men!
That is one of the reasons why I am inspired to write about this topic in depth! It is crucial to remain optimized as that will allow us to be the father, husband, employee, or CEO that will crush it daily and be someone people will look up to and that friends will like to have by their side, while their enemies will fear!
So if you feel like you have been underperforming recently, spend the next 5-10 minutes reading about testosterone, its functions, how to optimize it, and some of the common side effects of low testosterone.
What is testosterone?
Testosterone is an androgen hormone that is essential for the development and maintenance of male physical characteristics. It has many functions, like the development of our sexual organs and the development and preservation of muscle tissue. It also regulates our mood and affects cognitive function and decision-making.
Testosterone is made of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms. It contains ten carbon atoms, 28 hydrogen atoms, and two oxygen atoms.
How is testosterone produced in the male body?
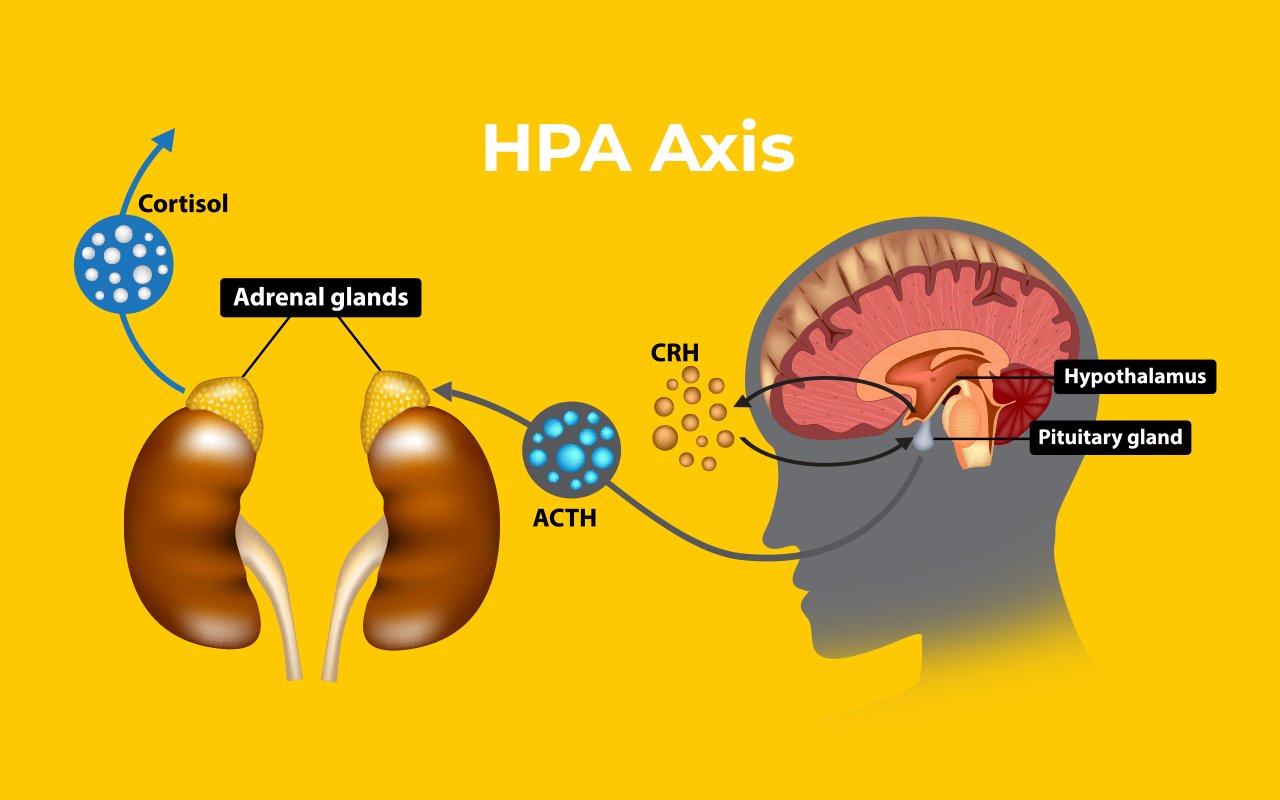
Testosterone is produced in the testes of men by the Leydig cells. The production of this vital hormone is regulated by a complex feedback system that involves the brain's hypothalamus and pituitary gland, as well as the testes themselves. This feedback system is called the HPA axis (hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis).
When the brain receives signals that testosterone levels are low, it releases hormones that signal to the testes to produce more of this hormone. When there is an abundance of testosterone, these signals turn off, and production stops.
That is why when you inject testosterone, your natural production tends to stop. More about that later in this article! Be careful about how much testosterone you take, the length of your cycle, and the post-cycle therapy you follow.
Breakdown of the testosterone production process
GnRH - gonadotropin-releasing hormone gets secreted by the hypothalamus. GnRH stimulates the pituitary gland to release follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH).
LH then travels through the bloodstream to the Leydig cells in the testes, stimulating testosterone production from cholesterol. On the other hand, FSH plays a role in the production of sperm cells in the testes.
A negative feedback system regulates the amount of testosterone produced by the Leydig cells. When testosterone levels in the blood are high, they signal to the hypothalamus and pituitary gland to decrease the production of GnRH, LH, and FSH. That helps to maintain a stable level of testosterone in the body.
Testosterone production peaks during adolescence and early adulthood and then gradually declines with age. Some factors affecting testosterone production include stress, obesity, and certain medical conditions or medications.
How to increase testosterone production?
Testosterone can be increased naturally by following lifestyle changes such as exercising regularly, eating a healthy diet, and getting adequate sleep every night. Exercises like weight lifting are beneficial for testosterone production as it helps increase the body's natural anabolic hormone. Some medical ways can help increase testosterone in men with testosterone deficiency. Let's first discuss the natural ways before we discuss testosterone replacement therapy and other medical ways to fix male hypogonadism.
Natural ways to increase testosterone in men
Exercise
Exercise is one of the most effective ways to increase testosterone levels naturally. Studies have shown that resistance training, such as weight lifting, can significantly increase testosterone levels in both men and women. Additionally, high-intensity interval training (HIIT) can also be effective in increasing testosterone levels.
Diet
Your diet can also have an impact on your testosterone levels. A diet high in protein and healthy fats, such as omega-3 fatty acids, can help increase testosterone levels. On the other hand, consuming a diet high in sugar and processed foods can decrease testosterone levels.
Sleep
Getting enough sleep is crucial for maintaining healthy testosterone levels. Studies have shown that lack of sleep can lower testosterone levels in men, sometimes leading to testosterone deficiency.
Stress management
Chronic stress can harm testosterone levels. Therefore, stress management techniques such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises can help increase testosterone levels.
Medical ways to increase testosterone
Testosterone Replacement Therapy (TRT)
TRT is a medical treatment that is growing in popularity and involves injecting testosterone into the body to replace the testosterone that the body produces in insufficient quantities. The injections can be given every two to four weeks or more frequently in smaller dosages, such as once per week, 2-3 times per week, or even daily. The dosage and frequency depend on the individual's preferences and should be determined by a healthcare professional.
Clomiphene Citrate
Clomiphene citrate is a medication used to treat infertility in women. It works by stimulating the production of testosterone in the body. However, it can also be used off-label to treat low testosterone in men.
HCG Injections
Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (HCG) injections are another option for increasing testosterone levels. HCG is a hormone that stimulates the testes to produce testosterone. The injections can be given two to three times per week.
I would note that TRT and other medical treatments for low testosterone should only be pursued with the guidance of an endocrinologist or other healthcare professional. These treatments can have potential side effects and risks, so working closely with a professional and weighing the side effects vs. benefits is essential to determine your best action.
Side effects of low testosterone levels
Common symptoms of low testosterone include low to non-existent sex drive and inability to preserve muscle mass or build new muscle tissue. Low testosterone levels can also cause depression, infertility, and erectile dysfunction. If you are experiencing any of these symptoms consistently, discussing them with your doctor is essential.
Learn more about the side effects of low testosterone in men: [Side Effects of Low Testosterone in Men]
Lifestyle factors that affect your testosterone levels negatively
Your testosterone levels can be negatively affected by a variety of lifestyle choices:
• Smoking
• Excessive alcohol consumption
• Poor diet or malnutrition
• Lack of physical activity
• Stress and anxiety
• Sleep deprivation
It is essential to ensure that you reduce or eliminate these factors to maintain healthy testosterone levels. Read further to find out the recommended values for testosterone and why it is not enough to test for total testosterone when conducting a blood test.
Normal testosterone levels per recommendations from The Endocrine Society
The Endocrine Society recommends the following values for total testosterone levels in the blood:
• Adult males aged 19-39: 270-1,070 ng/dL
• Adult males aged 40-59: 200-950 ng/dL
• Adult males aged 60 and over 150-700 ng/
It is important to note that some men might be within these ranges but might experience the symptoms of low testosterone. This next part is crucial for you to understand whether you might need testosterone therapy or not!
The Endocrine Society has lowered the recommendations for testosterone levels in men over the past 40 years! In 1984, the Endocrine Society's recommended lower limit for testosterone in men was 300 ng/dL, while in 2018, they lowered it to 264 ng/dL, representing a decrease of approximately 12% over 34 years.
That means that even if you are in today's recommended values, you might still have a testosterone deficiency if you are close to the lower border of the recommended testosterone values.
Let's say that you are within the recommended values or even at the higher end of the recommended values; you still might need testosterone treatment. Let me explain why!
When you do a blood test, you must test both for total testosterone and something called free testosterone, and I will explain why!
Total testosterone represents the total available testosterone in your bloodstream, but not all of that is available for your body to use.
Free testosterone represents the amount of testosterone available for your tissues and organs. Therefore, testing both total and free testosterone levels is essential when assessing whether one might need hormone treatment.
The Endocrine Society recommends the following reference ranges for free testosterone levels in ng/dL:
Adult men (19 years and older): 5.0-21.0 ng/dL
Finally, an individual's response to testosterone therapy varies greatly, and individuals should discuss the potential risks and benefits of testosterone therapy with their healthcare professional before proceeding. Regular follow-up visits are essential to monitor side effects and adjust dosages accordingly. A healthcare professional can help determine if TRT or other treatments are necessary and assist in properly managing them.
It is also essential for individuals to understand that the benefits of testosterone therapy are not immediate, and it may take several weeks before any changes in symptoms become apparent. Therefore, it is essential to remain patient and open-minded when considering testosterone therapy.
With proper evaluation and management, testosterone can be a safe and effective treatment for those with low levels. Discussing your symptoms with your healthcare professional is the best way to determine if testosterone therapy is right for you.
To read more about the potential side effects of testosterone replacement therapy, click here!
Common questions and answers
What impact does testosterone level have on my muscle-building capacities?
The relationship between testosterone and muscle building is complex. While higher testosterone levels can lead to more significant muscle growth, increasing testosterone levels through supplements or other means may not necessarily result in substantial muscle gains. Instead, building muscle requires a combination of proper nutrition, consistent training, and adequate rest and recovery.
Does testosterone therapy increase the likelihood of getting prostate cancer?
That is a question that has caused a lot of debate amongst people in the scientific as well as fitness community. However, no scientific data supports the claim that TRT increases prostate cancer risk. The most comprehensive study to date was published in the Journal of the American Medical Association in 2015, followed over 44,000 men for up to 20 years, and found no increased risk of prostate cancer in men who received TRT.
Why is it important to measure my sex hormone-binding globulin when on testosterone replacement therapy?
SHBG is a protein that binds to your testosterone and estrogen in the bloodstream. Therefore if you have high levels of SHGB, they can bind to your testosterone and make it inactive. That's why it is crucial to monitor your sex hormone-binding globulin levels when on TRT. Please do not hesitate to leave questions related to the topic in the comments section below!